ソリューション・エクスプローラー構成
complex_value.h
#ifndef COMPLEX_VALUE_H
#define COMPLEX_VALUE_H
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
/**
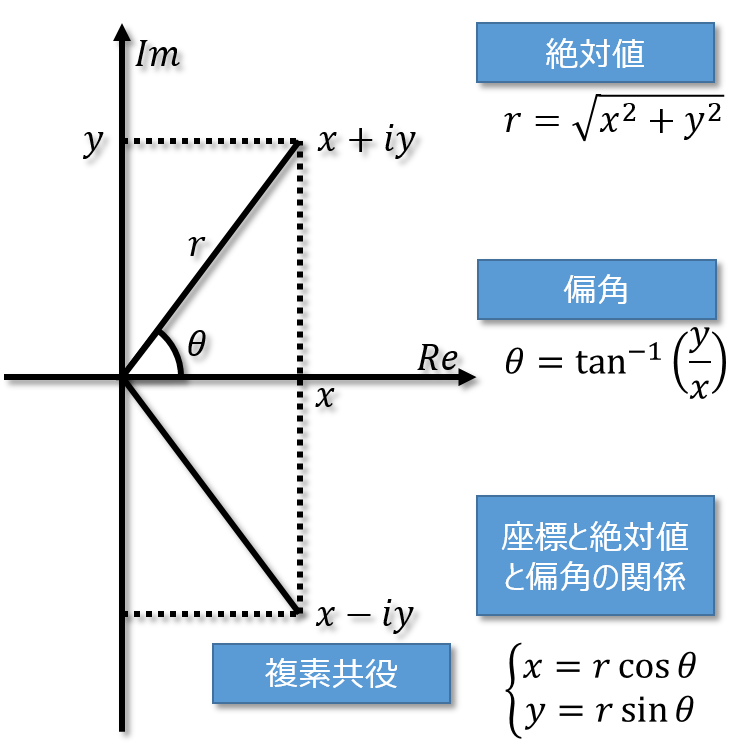
* @struct complex_number
* @breif 複素数を表現する構造体
*/
struct complex_number {
double real; /**< 実数部 */
double imag; /**< 虚数部 */
};
/**
* @brief 複素数の表示
* @param a 表示する複素数
*/
void complex_number_print(struct complex_number a);
/**
* @breif 複素数の加算
* @param a 複素数
* @param b 複素数
* @return a + b
*/
struct complex_number
complex_number_add(struct complex_number a, struct complex_number b);
/**
* @brief 複素数の減算
* @param a 複素数
* @param b 複素数
* @return a - b
*/
struct complex_number
complex_number_sub(struct complex_number a, struct complex_number b);
/**
* @brief 複素数の乗算
* @param a 複素数
* @param b 複素数
* @return a * b
*/
struct complex_number
complex_number_mul(struct complex_number a, struct complex_number b);
/**
* @brief 複素数の除算
* @param a 複素数
* @param b 複素数
* @return a / b
*/
struct complex_number
complex_number_div(struct complex_number a, struct complex_number b);
/**
* @breif 複素数の実部と虚部を与えて複素数を返す
* @param real 複素数の実部
* @param imag 複素数の虚部
* @return (real) + (imag) i
*/
struct complex_number
complex_number_new(double real, double imag);
/**
* @biref 複素数の実部
* @param a 複素数
* @return 複素数aの実部 ( real )
*/
double
complex_number_real(struct complex_number a);
/**
* @brief 複素数の虚部
* @param a 複素数
* @return 複素数aの虚部 ( imag )
*/
double
complex_number_imag(struct complex_number a);
/**
* @brief 複素数の共役
* @param a 複素数
* @return Re{a} - Im{a} i
*/
struct complex_number
complex_number_conj(struct complex_number a);
/**
* @brief 複素数の絶対値
* @param a 複素数
* @retval |a|
*/
double
complex_number_abs(struct complex_number a);
/**
* @breif 複素数の偏角
* @param a 複素数
* @return arctan(Im{a}/Re{a})
*/
double
complex_number_arg(struct complex_number a);
/**
* @brief 絶対値と偏角を与えて複素数を返す
* @param abs 絶対値
* @param arg 偏角
* @return (abs)*cos(arg) + (abs)*sin(arg) i
*/
struct complex_number
complex_number_polar(double abs, double arg);
#endif /* COMPLEX_H */
|
complex_value.c
#include "complex_value.h"
void
complex_number_print(struct complex_number a) {
if (a.imag < 0) {
printf("%f%fi", a.real, a.imag);
} else {
printf("%f+%fi", a.real, a.imag);
}
}
struct complex_number
complex_number_add(struct complex_number a, struct complex_number b) {
struct complex_number result;
result.real = a.real + b.real;
result.imag = a.imag + b.imag;
return result;
}
struct complex_number
complex_number_sub(struct complex_number a, struct complex_number b) {
struct complex_number result;
result.real = a.real - b.real;
result.imag = a.imag - b.imag;
return result;
}
struct complex_number
complex_number_mul(struct complex_number a, struct complex_number b) {
struct complex_number result;
result.real = a.real * b.real - a.imag * b.imag;
result.imag = a.real * b.imag + a.imag * b.real;
return result;
}
struct complex_number
complex_number_div(struct complex_number a, struct complex_number b) {
struct complex_number result = {0.0, 0.0};
double d;
d = b.real * b.real + b.imag * b.imag;
if (d == 0.0) {
printf("divided by zero\n");
return result;
}
result.real = (a.real * b.real + a.imag * b.imag) / d;
result.imag = (-a.real * b.imag + a.imag * b.real) / d;
return result;
}
struct complex_number
complex_number_new(double real, double imag) {
/* ここを実装せよ */
}
double
complex_number_real(struct complex_number a) {
/* ここを実装せよ */
}
double
complex_number_imag(struct complex_number a) {
/* ここを実装せよ */
}
struct complex_number
complex_number_conj(struct complex_number a) {
/* ここを実装せよ */
}
double
complex_number_abs(struct complex_number a) {
/* ここを実装せよ */
}
double
complex_number_arg(struct complex_number a) {
/* ここを実装せよ */
}
struct complex_number
complex_number_polar(double abs, double arg) {
/* ここを実装せよ */
}
|
complex_test.c
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "complex_value.h"
int
main(void) {
struct complex_number z;
double abs, arg;
/* 適当な複素数を設定 */
z = complex_number_new(3.0, 4.0);
/* zを表示 */
printf("z = ");
complex_number_print(z);
printf("\n");
/* zの複素共役を表示 */
printf("conj(z) = ");
complex_number_print(complex_number_conj(z));
printf("\n");
/* zの絶対値を表示 */
abs = complex_number_abs(z);
printf("abs(z) = %f\n", abs);
/* zの偏角を表示 */
arg = complex_number_arg(z);
printf("arg(z) = %f\n", arg);
/* absとargを与えて複素数を表示 */
printf("polar(abs,arg) = ");
complex_number_print(complex_number_polar(abs, arg));
printf("\n");
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
|
|
出力例
z = 3.000000+4.000000i conj(z) = 3.000000-4.000000i abs(z) = 5.000000 arg(z) = 0.927295 polar(abs,arg) = 3.000000+4.000000i
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
/* 1次元配列の要素の合計を計算する関数 */
int
sum_vec(int a[], int m) { // 1次元配列を関数に渡す場合、その要素数は省略できるので、配列の長さに対して汎用な関数を作成することが可能
int i;
int x = 0;
for (i = 0; i < m; i++) {
x += a[i];
}
return x;
}
/* 2次元配列の要素の合計を計算する関数 */
int
sum_mat(int a[][3], int n) { // 2次元以上の配列を関数に渡す場合,配列の構造を関数の引数に指示してやる必要があるので汎用な関数を作成することは不可能(a[][]とは出来ない)
int i, j;
int x = 0;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
x += a[i][j];
}
}
return x;
}
int
main(void) {
int M = 3;
int N = 2;
int a[3] = {1, 2, 3};
int b[2][3] = {
{1, 2, 3},
{4, 5, 6}};
printf("1次元配列aの要素の合計値は %d\n", sum_vec(a, M)); /* 1次元配列を関数に渡す */
printf("2次元配列bの要素の合計値は %d\n", sum_mat(b, N)); /* 2次元配列を関数に渡す */
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
ソリューション・エクスプローラー構成
vector.h
#ifndef VECTOR_H
#define VECTOR_H
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
/**
* @struct vector
* @brief 1次元配列構造体
*/
typedef struct {
int size; /**< サイズ */
double* val; /**< 配列要素 */
} vector;
/**
* @brief サイズnの1次元配列を動的に確保
* @param[in] n サイズ
* @param[out] vec 1次元配列
*/
void vector_new(int n, vector* vec);
/**
* @brief 確保した1次元配列を開放
* @param[in,out] vec 開放する1次元配列
*/
void vector_delete(vector* vec);
/**
* @brief 1次元配列vec2をvec1にコピー
* @param[out] vec1 コピー先
* @param[in] vec2 コピー元
* @retval 1 成功
* @retval 0 失敗(vec1とvec2のサイズ不整合)
*/
int vector_copy(vector* vec1, const vector* vec2);
/**
* @breif 1次元配列vecをformatに従って標準出力に表示
* @param[in] vec 出力する1次元配列
* @param[in] format 出力形式(prinfの第1引数)
*/
void vector_print(const vector* vec, const char* format);
#endif /* VECTOR_H */
|
vector.c
#include "vector.h"
void vector_new(int n, vector* vec) {
if (n <= 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "allocation failure in vector_new()\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
} else {
vec->val = (double*) malloc(n * sizeof (double));
if (vec->val == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "allocation failure in vector_new()\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
vec->size = n;
}
}
void vector_delete(vector* vec) {
free(vec->val);
}
int vector_copy(vector* vec1, const vector* vec2) {
int i;
if (vec1->size != vec2->size) {
return 0;
}
for (i = 0; i < vec1->size; ++i) {
vec1->val[i] = vec2->val[i];
}
return 1;
}
void vector_print(const vector* vec, const char* format) {
int i;
printf("[");
for (i = 0; i < vec->size; ++i) {
printf(format, vec->val[i]);
if (i < vec->size - 1) {
printf(", ");
}
}
printf("]\n");
}
|
vector_test.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "vector.h"
int main(void) {
int n;
vector vec1, vec2;
/* 1次元配列のサイズ設定 */
n = 4;
/* vec1の領域確保 */
vector_new(n, &vec1);
/* 要素の代入 */
vec1.val[0] = 0.2;
vec1.val[1] = 1.3;
vec1.val[2] = 2.5;
vec1.val[3] = 3.6;
/* vec1の要素の表示 */
printf("vec1 = ");
vector_print(&vec1, "%f");
/* vec2の領域確保 */
vector_new(n, &vec2);
/* 1次元配列の要素のコピー */
if (vector_copy(&vec2, &vec1)) {
/* vec2の要素の表示 */
printf("vec2 = ");
vector_print(&vec2, "%f");
}
/* 領域の開放 */
vector_delete(&vec1);
vector_delete(&vec2);
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
|
|
出力例
vec1 = [0.200000, 1.300000, 2.500000, 3.600000] vec2 = [0.200000, 1.300000, 2.500000, 3.600000]
ソリューション・エクスプローラー構成
matrix.h
#ifndef MATRIX_H
#define MATRIX_H
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
/**
* @struct matrix
* @brief 2次元配列構造体
*/
typedef struct {
int size1; /**< 行数 */
int size2; /**< 列数 */
double** val; /**< 配列要素 */
} matrix;
/**
* @brief m×nの2次元配列を動的に確保
* @param[in] m 行数
* @param[in] n 列数
* @param[out] mat 2次元配列
*/
void matrix_new(int m, int n, matrix* mat);
/**
* @brief 確保した2次元配列を開放
* @param[in,out] mat 開放する2次元配列
*/
void matrix_delete(matrix* mat);
/**
* @brief 2次元配列mat2をmat1にコピー
* @param[out] mat1 コピー先
* @param[in] mat2 コピー元
* @retval 1 成功
* @retval 0 失敗(mat1とmat2のサイズ不整合)
*/
int matrix_copy(matrix* mat1, const matrix* mat2);
/**
* @brief 2次元配列matをformatに従って標準出力に表示
* @param[in] mat 出力する2次元配列
* @param[in] format出力形式(prinfの第1引数)
*/
void matrix_print(const matrix* mat, const char* format);
#endif /* MATRIX_H */
|
matrix.c
#include "matrix.h"
void matrix_new(int m, int n, matrix* mat) {
int i;
if ((m <= 0) || (n <= 0)) {
fprintf(stderr, "allocation failure in matrix_new()\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
mat->val = (double**) malloc(m * sizeof (double*));
if (mat->val == NULL) { /* 領域割当に失敗したら */
fprintf(stderr, "allocation failure in matrix_new()\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
for (i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
mat->val[i] = (double*) malloc(n * sizeof (double));
if (mat->val[i] == NULL) { /* 領域割当に失敗したら */
while (--i >= 0) {
free(mat->val[i]); /* 領域開放 */
}
free(mat->val);
fprintf(stderr, "allocation failure in matrix_new()\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
}
mat->size1 = m;
mat->size2 = n;
}
void matrix_delete(matrix* mat) {
int i;
for (i = 0; i < mat->size1; ++i) {
free(mat->val[i]);
}
free(mat->val);
mat->size1 = mat->size2 = 0;
}
int matrix_copy(matrix* mat1, const matrix* mat2) {
int i, j;
if ((mat1->size1 != mat2->size1) || (mat2->size2 != mat2->size2)) {
return 0;
}
for (i = 0; i < mat1->size1; ++i) {
for (j = 0; j < mat1->size2; ++j) {
mat1->val[i][j] = mat2->val[i][j];
}
}
return 1;
}
void matrix_print(const matrix* mat, const char* format) {
int i, j;
printf("[");
for (i = 0; i < mat->size1; ++i) {
for (j = 0; j < mat->size2; ++j) {
printf(format, mat->val[i][j]);
if (j < mat->size2 - 1) {
printf(", ");
}
}
if (i == mat->size1 - 1) {
printf("]");
}
printf("\n");
}
}
|
matrix_test.c
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "matrix.h"
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
int i, j;
int m, n;
matrix mat1, mat2;
/* 2次元配列の大きさ設定 */
m = 3;
n = 4;
/* mat1の領域確保 */
matrix_new(m, n, &mat1);
/* 要素の代入 */
for (i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
mat1.val[i][j] = (i * 7 + 3 * j) - 5;
}
}
/* mat1の表示 */
printf("mat1 = \n");
matrix_print(&mat1, "%f");
/* mat2の領域確保 */
matrix_new(m, n, &mat2);
/* 2次元配列の要素のコピー */
if (matrix_copy(&mat2, &mat1)) {
/* mat2の表示 */
printf("mat2 = \n");
matrix_print(&mat2, "%f");
}
/* 領域の開放 */
matrix_delete(&mat1);
matrix_delete(&mat2);
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
|
|
出力例
mat1 = [-5.000000, -2.000000, 1.000000, 4.000000 2.000000, 5.000000, 8.000000, 11.000000 9.000000, 12.000000, 15.000000, 18.000000] mat2 = [-5.000000, -2.000000, 1.000000, 4.000000 2.000000, 5.000000, 8.000000, 11.000000 9.000000, 12.000000, 15.000000, 18.000000]
ソリューション・エクスプローラー構成
array_utils.h #ifndef ARRAY_UTILS_H #define ARRAY_UTILS_H #include "vector.h" #include "matrix.h" /** * @breif vec1 = vec2 + vec3 * @param[out] vec1 1次元配列(vec2+vec3で上書きされる) * @param[in] vec2 1次元配列 * @param[in] vec3 1次元配列 * @retval 1 成功 * @retval 0 失敗(vec1,vec2,vec3のサイズ不整合) */ int array_utils_vector_add(vector* vec1, const vector* vec2, const vector* vec3); /** * @breif vec1 = vec2 - vec3 * @param[out] vec1 1次元配列(vec2+vec3で上書きされる) * @param[in] vec2 1次元配列 * @param[in] vec3 1次元配列 * @retval 1 成功 * @retval 0 失敗(vec1,vec2,vec3のサイズ不整合) */ int array_utils_vector_sub(vector* vec1, const vector* vec2, const vector* vec3); /** * @breif mat1 = mat2 + mat3 * @param[out] mat1 2次元配列(mat2+mat3で上書きされる) * @param[in] mat2 2次元配列 * @param[in] mat3 2次元配列 * @retval 1 成功 * @retval 0 失敗(mat1,mat2,mat3のサイズ不整合) */ int array_utils_matrix_add(matrix* mat1, const matrix* mat2, const matrix* mat3); /** * @breif mat1 = mat2 - mat3 * @param[out] mat1 2次元配列(mat2+mat3で上書きされる) * @param[in] mat2 2次元配列 * @param[in] mat3 2次元配列 * @retval 1 成功 * @retval 0 失敗(mat1,mat2,mat3のサイズ不整合) */ int array_utils_matrix_sub(matrix* mat1, const matrix* mat2, const matrix* mat3); /** * @breif mat1 = mat2 * mat3 * @param[out] mat1 2次元配列(mat2*mat3で上書きされる) * @param[in] mat2 2次元配列 * @param[in] mat3 2次元配列 * @retval 1 成功 * @retval 0 失敗(mat1,mat2,mat3のサイズ不整合) */ int array_utils_matrix_mul(matrix* mat1, const matrix* mat2, const matrix* mat3); /** * @breif vec1 = mat * vec2 * @param[out] vec1 1次元配列(mat*vec2で上書きされる) * @param[in] mat 2次元配列 * @param[in] vec2 1次元配列 * @retval 1 成功 * @retval 0 失敗(vec1,mat,vec2;のサイズ不整合) */ int array_utils_matrix_vector_mul(vector* vec1, const matrix* mat, const vector* vec2); #endif /* ARRAY_UTILS_H */ |
array_utils.c
#include "array_utils.h"
int array_utils_vector_add(vector* vec1, const vector* vec2, const vector* vec3) {
int i;
if ((vec1->size != vec2->size) || (vec1->size != vec3->size)) {
return 0;
}
for (i = 0; i < vec1->size; ++i) {
vec1->val[i] = vec2->val[i] + vec3->val[i];
}
return 1;
}
int array_utils_vector_sub(vector* vec1, const vector* vec2, const vector* vec3) {
/* ここを実装せよ */
}
int array_utils_matrix_add(matrix* mat1, const matrix* mat2, const matrix* mat3) {
int i, j;
if ((mat1->size1 != mat2->size1) || (mat1->size1 != mat3->size1) || (mat1->size2 != mat2->size2) || (mat1->size2 != mat3->size2)) {
return 0;
}
for (i = 0; i < mat1->size1; ++i) {
for (j = 0; j < mat1->size2; ++j) {
mat1->val[i][j] = mat2->val[i][j] + mat3->val[i][j];
}
}
return 1;
}
int array_utils_matrix_sub(matrix* mat1, const matrix* mat2, const matrix* mat3) {
/* ここを実装せよ */
}
int array_utils_matrix_mul(matrix* mat1, const matrix* mat2, const matrix* mat3) {
int i, j, k;
if ((mat1->size1 != mat2->size1) || (mat1->size2 != mat3->size2) || (mat2->size2 != mat3->size1)) {
return 0;
}
for (i = 0; i < mat1->size1; ++i) {
for (j = 0; j < mat1->size2; ++j) {
mat1->val[i][j] = 0.0;
for (k = 0; k < mat2->size2; ++k) {
mat1->val[i][j] += mat2->val[i][k] * mat3->val[k][j];
}
}
}
return 1;
}
int array_utils_matrix_vector_mul(vector* vec1, const matrix* mat, const vector* vec2) {
/* ここを実装せよ */
}
|
array_utils_test.c
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "array_utils.h"
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
int i, j;
int l, m, n;
vector vec1, vec2, vec3, vec4;
matrix mat1, mat2, mat3, mat4, mat5;
/* ベクトル・行列サイズ */
l = 3;
m = 2;
n = 3;
/* ベクトル */
vector_new(n, &vec1);
vector_new(n, &vec2);
vector_new(n, &vec3);
vector_new(m, &vec4);
/* 行列 */
matrix_new(m, n, &mat1);
matrix_new(m, n, &mat2);
matrix_new(m, n, &mat3);
matrix_new(l, m, &mat4);
matrix_new(l, n, &mat5);
printf("##### vector #####\n");
/* vec1の初期化 */
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
vec1.val[i] = 3 * i + 1;
}
/* vec1の表示 */
printf("vec1 = ");
vector_print(&vec1, "%f");
/* vec1をvec2にコピー */
vector_copy(&vec2, &vec1);
/* vec2の表示 */
printf("vec2 = ");
vector_print(&vec2, "%f");
/* vec3 = vec1 + vec2 */
array_utils_vector_add(&vec3, &vec1, &vec2);
/* vec3の表示 */
printf("vec3 = vec1 + vec2 = ");
vector_print(&vec3, "%f");
/* vec3 = vec1 - vec2 */
array_utils_vector_sub(&vec3, &vec1, &vec2);
/* vec3の表示 */
printf("vec3 = vec1 - vec2 = ");
vector_print(&vec3, "%f");
printf("##### matrix #####\n");
/* mat1の初期化 */
for (i = 0; i < mat1.size1; ++i) {
for (j = 0; j < mat1.size2; ++j) {
mat1.val[i][j] = i + j;
}
}
/* mat1の表示 */
printf("mat1 =\n");
matrix_print(&mat1, "%f");
/* mat1をmat2にコピー */
matrix_copy(&mat2, &mat1);
/* mat2の表示 */
printf("mat2 =\n");
matrix_print(&mat2, "%f");
/* mat3 = mat1 + mat2*/
array_utils_matrix_add(&mat3, &mat1, &mat2);
/* mat3の表示 */
printf("mat3 =\n");
matrix_print(&mat3, "%f");
/* mat3 = mat1 - mat2*/
array_utils_matrix_sub(&mat3, &mat1, &mat2);
/* mat3の表示 */
printf("mat3 =\n");
matrix_print(&mat3, "%f");
printf("##### vector & matrix #####\n");
/* mat4の初期化 */
for (i = 0; i < mat4.size1; ++i) {
for (j = 0; j < mat4.size2; ++j) {
mat4.val[i][j] = i + j;
}
}
/* mat4の表示 */
printf("mat4 =\n");
matrix_print(&mat4, "%f");
/* mat5 = mat4 * mat1 */
array_utils_matrix_mul(&mat5, &mat4, &mat1);
/* mat5の表示 */
printf("mat5 =\n");
matrix_print(&mat5, "%f");
/* vec4 = mat1 * vec1 */
array_utils_matrix_vector_mul(&vec4, &mat1, &vec1);
/* vec4の表示 */
printf("vec4 = ");
vector_print(&vec4, "%f");
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
|
|
出力例
##### vector ##### vec1 = [1.000000, 4.000000, 7.000000] vec2 = [1.000000, 4.000000, 7.000000] vec3 = vec1 + vec2 = [2.000000, 8.000000, 14.000000] vec3 = vec1 - vec2 = [0.000000, 0.000000, 0.000000] ##### matrix ##### mat1 = [0.000000, 1.000000, 2.000000 1.000000, 2.000000, 3.000000] mat2 = [0.000000, 1.000000, 2.000000 1.000000, 2.000000, 3.000000] mat3 = [0.000000, 2.000000, 4.000000 2.000000, 4.000000, 6.000000] mat3 = [0.000000, 0.000000, 0.000000 0.000000, 0.000000, 0.000000] ##### vector & matrix ##### mat4 = [0.000000, 1.000000 1.000000, 2.000000 2.000000, 3.000000] mat5 = [1.000000, 2.000000, 3.000000 2.000000, 5.000000, 8.000000 3.000000, 8.000000, 13.000000] vec4 = [18.000000, 30.000000]